This is 2nd part of the series where we are discussing the importance of SQL for Data Scientist and how we can utilize it for our project’s data requirement.
ORDER BY & SUBQUERY
ORDER BY is used to sort the results of a SQL query in ascending or descending order based on one or more columns.
We will consider below table for illustration purpose:
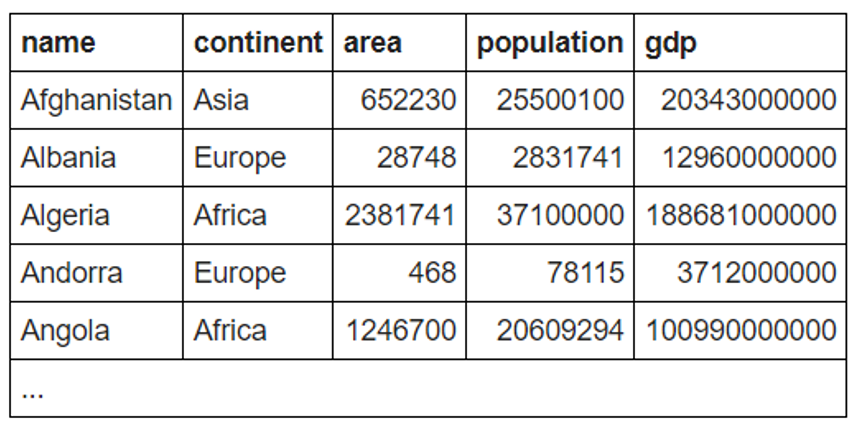
Each row is representing area, population and GDP of a country along with the continent it belongs to and the table name is world.
If the column which we want to sort is having numerical data, then ORDER BY sorts it on the basis of its value whereas if the data is not numerical then it sorts on alphabetical order.
By default, ORDER BY sorts in ascending order and if the requirement is to sort in descending we would have to include DESC in the query.
For example, if we want to sort the world table from lowest gdp to highest, we can achieve this with the below query:

The query is simple and we need to include ORDER BY at the end with the column on which we want the data to be sorted by. By default, ORDER BY sorts in ascending order so the lowest gdp country will be at the top. Below is the snippet of output of the above query:
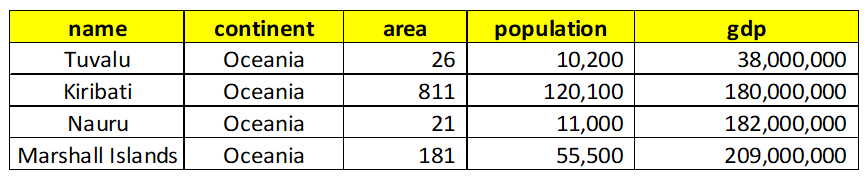
Tuvalu is the country with the least gdp.
What will be the query if we want to sort world table with highest gdp country at the top that is in descending order?
We simply need to add DESC clause along with order by in the above query so that the world table gets sorted in descending order of gdp.
Below is the query and output:
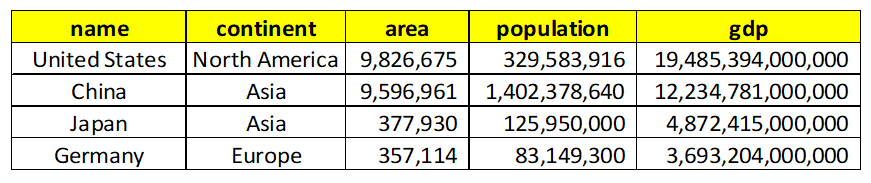
United States is the country with the highest GDP.
SUBQUERY
Subquery is a method in which we include a query inside a query to obtain the final requirement.
From above, we saw that United States is the country with the highest GDP, what if the requirement is to get the country name from the world table with highest GDP?
One of the ways to achieve the above requirement is to use SUBQUERY, remember that, SUBQUERY is not a syntax like ORDER BY and LIMIT, it’s a method or way to write a final query to obtain the final data requirement.
Below is the query:
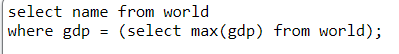
The above query will return United States as we have selected name where gdp is equal to maximum gdp present in the world table.
Now, the question is where did we use SUBQUERY? It is nowhere to be seen in the above query.
(select max(gdp) from world) is the SUBQUERY because this is a query in itself as it will return the maximum gdp value from world table but in the overall query it is being used as a filter medium in the WHERE clause to get the name (country), that is why it is called SUBQUERY of the final QUERY.
IF & CASE WHEN
IF is used to create a new column based on some conditions on one or more columns (features). Let’s say, you want to categorize population of a country like High and Low Population where you call a country high population country if its population is greater than 20M and low otherwise. So, basically, you have a created a condition on population column. This categorization can be achieved by below query and output:

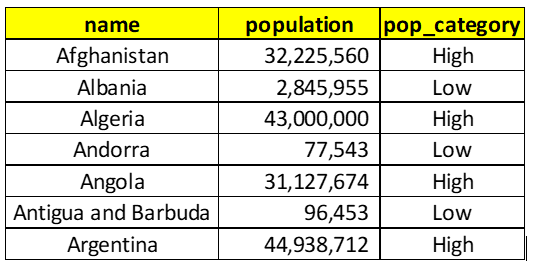
Flow of if query execution works like if population>20000000 then High else Low, at first place after IF clause, we write if the condition is True and at the second place we write if the condition is False same as if population>20M then High else Low.
CASE WHEN is similar to IF but it is handy when we have to create multiple categories based on conditions on one or more columns. Let’s say we have to create population categories High, Medium and Low, then if you look at IF syntax, we don’t have space to include Medium in the same query because it can accommodate only two parameters in a single IF statement. Although, we can include one more IF clause inside this IF to accommodate Medium category which is also called Nested IF (IF clause inside an IF clause) but it will increase the complexity of the query and it will be very inefficient way to write code when number of categories will be more. When the number of categories is more than 2 then CASE WHEN should be preferred over IF. Let’s say the new requirement is we will call a country Low population when it’s population<20M, Medium when itis between 20M and 40M (both inclusive) and High when>40M.
Below is the query and required result:

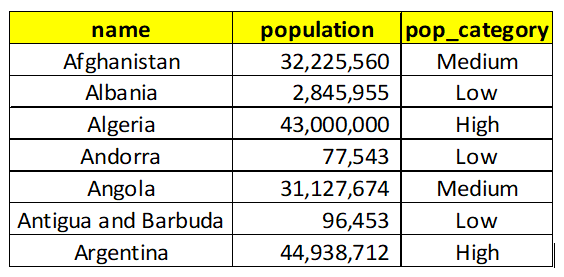
We are able to include multiple categories and query is also easy to read and understand. CASE WHEN works like when some condition is True THEN it will return a particular value, if some other condition is True THEN it will return some other value and finally it should be closed by END to inform the query that we don’t need more categories. It can be easily scaled to include more categories, let’s say you have to include Very High category, then easily one more WHEN statement can be included in the same query without increasing the complexity of the existing query.
Below is the example code:

[References]: https://sqlzoo.net/ for dataset and code window
